[CA] Chapter 1-2: MIPS(MAPS)
[CA] Chapter 1-2: MIPS(MAPS)
⚙ Computer Architecture 공부
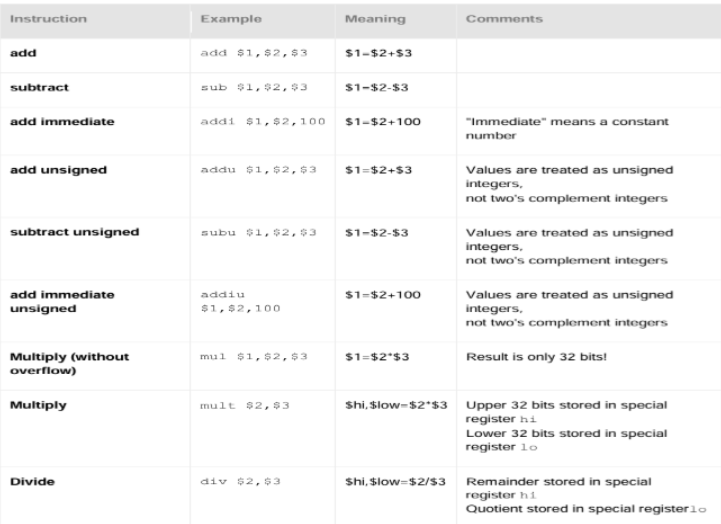
MIPS Arithmetic Instructions
부호 있는 연산(signed)(
add,sub): 음수 표현이 가능한 2의 보수(two’s complement) 방식으로 연산. 오버플로우 확인
부호 없는 연산(unsigned)(addu,subu): 모든 비트를 양수로 취급. 오버플로우 확인X.
mult: 32bits × 32bits = 최대 64bits 결과가 나올 수 있어 special register(hi,lo)를 사용.
hi: 상위 32bits 저장lo: 하위 32bits 저장div: 나눗셈 결과는 두 부분으로 나뉨.
lo: 몫(quotient) 저장hi: 나머지(remainder) 저장
Example: FACTORIAL OF N
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 팩토리얼 계산 예제(n! 계산)
# 입력: $s1 = n
# 출력: $t0 = n!
move $t0, $s1 # result = n
addi $s1, $s1, -1 # n = n - 1
factorial_loop:
mul $t0, $t0, $s1 # result *= n
addi $s1, $s1, -1 # n -= 1
bne $s1, $zero, factorial_loop # if n != 0, repeat
- Branch Instructions:
bne $s1, $zero, factorial_loop: $s1 값이 0이 아니면 factorial_loop 레이블로 점프- 기타 branch instructions -
beq src1, src2, label: 두 값이 같으면 branch (Branch if Equal)
MARS Simulation
MIPS 프로그램은 두 가지 주요 세그먼트로 구성된다.
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
12
13
14
# 기본 MIPS 프로그램 템플릿
.text # text segment 시작
main: # 프로그램 시작점
# 여기에 명령어 작성
# 프로그램 종료
li $v0, 10 # exit 시스템 콜 코드
syscall # 시스템 콜 실행
.data # data segment 시작
# 여기에 변수 정의
message: .asciiz "Hello, World\n" # 문자열 변수
array: .word 1, 2, 3, 4, 5 # 정수 배열
# 이 밑에는 function .text 작성가능
text segment(.text)
- 실행 가능한 code 저장
- 주요 요소:
- main: 프로그램 시작점
- 레이블: 함수나 점프 위치를 표시 (예:
factorial_loop:) - 명령어: 실제 실행할 MIPS 명령어들
Data segment(.data)
- 정적 데이터(변수) 저장
- 데이터 타입:
.asciiz: null로 끝나는 문자열 (예:message: .asciiz "Hello").ascii: null로 끝나지 않는 문자열.word: 32비트 정수 (예:array: .word 1, 2, 3, 4).half: 16비트 정수.byte: 8비트 정수.space n: n바이트 공간 할당
System Calls
- MIPS에서는
syscall명령어를 사용하여 운영체제 서비스 호출 가능 - 주요 syscall code:
$v0 = 1: 정수 출력 (인자:$a0= 출력할 정수)$v0 = 4: 문자열 출력 (인자:$a0= 문자열 주소)$v0 = 5: 정수 입력 (반환:$v0= 입력된 정수)$v0 = 8: 문자열 입력 (인자:$a0= 버퍼 주소,$a1= 버퍼 길이)$v0 = 10: **프로그램 종료 **
- 합 계산 예제
1
2
3
4
5
6
7
8
9
10
11
# 1 + 2 + 3 + ... + n 계산
# 입력: $s1 = n
# 출력: $t0 = 합계
move $t0, $zero # 합계 초기화: sum = 0
move $t1, $zero # 카운터 초기화: i = 0
loop:
addi $t1, $t1, 1 # i = i + 1
add $t0, $t0, $t1 # sum = sum + i
bne $t1, $s1, loop # i != n이면 반복
카운터 증가:
addi $t1, $t1, 1
현재 카운터 값을 합계에 추가:add $t0, $t0, $t1
반복 조건 확인:bne $t1, $s1, loop
This post is licensed under CC BY 4.0 by the author.